In the world of electronics, transistors are the unsung heroes. These tiny semiconductor devices play a pivotal role in amplifying signals, switching circuits on and off, and serving as the fundamental building blocks of electronic devices. Whether you’re an aspiring engineer, a hobbyist, or just curious about how your gadgets work, this article will unravel the mysteries of transistors in basic electronics.
Introduction to Transistors
Transistors, often abbreviated as “BJTs” and “FETs,” are the fundamental components in electronic circuits. They were invented in the mid-20th century and have since revolutionized the electronics industry. Transistors are primarily used to amplify weak electronic signals and act as switches to control the flow of current in electronic devices.
Types of Transistors
Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
BJTs are one of the two main types of transistors. They come in two variants: NPN (Negative-Positive-Negative) and PNP (Positive-Negative-Positive). BJTs are commonly used in amplifier circuits and can be employed as switches in some applications.
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs)
FETs are the other main type of transistor. They operate based on the voltage applied to the gate terminal. FETs are widely used in integrated circuits and are crucial in digital electronics.
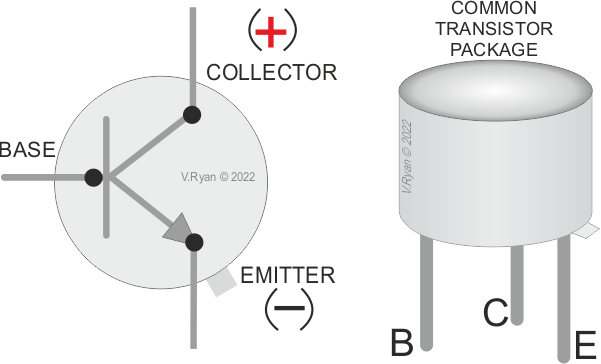
Transistor Symbols and Notations
Understanding transistor symbols and notations is essential when reading electronic schematics. These symbols represent the different transistor types and their configurations.
Transistor Operation
Amplification with Transistors
One of the primary functions of transistors is signal amplification. They can make weak signals stronger, a crucial aspect in audio and radio applications.
Transistor as a Switch
Transistors can also act as electronic switches. By controlling the voltage at their base (for BJTs) or gate (for FETs), you can turn the current flow on and off in other parts of the circuit.
Transistor Characteristics
Voltage and Current Relationships
Understanding the voltage and current relationships in transistors is key to their proper operation. These relationships are described by various equations and graphs.
Gain and Amplification Factors
Transistors exhibit gain, which is the ratio of output current or voltage to the input current or voltage. Gain plays a crucial role in amplifiers.
Applications of Transistors
Transistors find applications in various electronic devices:
In Amplifiers
Transistors are the heart of audio and radio amplifiers, making them essential components in music systems and communication devices.
In Oscillators
Oscillators use transistors to generate continuous waveforms, important in radio frequency and clock circuits.
In Digital Logic Circuits
Transistors serve as the building blocks of digital logic circuits, forming the basis of modern computing devices.
Transistor Biasing
Biasing is the process of applying a specific voltage to a transistor’s terminals to ensure it operates in the desired region. Proper biasing is critical for transistor stability.
Common Transistor Circuits
Common Emitter Amplifier
The common emitter amplifier configuration is widely used in electronic circuits for its high gain and versatility.
Common Base Amplifier
The common base amplifier configuration is suitable for high-frequency applications and low input impedance.
Common Collector Amplifier
The common collector amplifier configuration offers unity voltage gain but high current gain, making it suitable for impedance matching.
Transistor Testing and Troubleshooting
Learn how to test transistors and diagnose common issues in electronic circuits involving transistors.
Transistor Advancements
Integrated Circuits (ICs)
ICs, which incorporate multiple transistors on a single chip, have revolutionized electronics, leading to the development of smaller and more powerful devices.
Moore’s Law and Miniaturization
Moore’s Law predicts the doubling of transistor density on integrated circuits every two years, driving the miniaturization of electronics.
Challenges in Transistor Technology
Despite their incredible success, transistors face challenges, including heat dissipation and quantum effects, as they continue to shrink in size.
Future of Transistors
Explore the possibilities of future transistor technologies, including quantum transistors and novel materials.
Conclusion
Transistors are the unsung heroes of the electronics world. They have shaped the modern technological landscape, enabling the development of powerful computers, smartphones, and countless other devices. Understanding the fundamentals of transistors is a crucial step for anyone interested in electronics.

